WebFlux
非阻塞,更高的性能
函数式编程
响应式:区别于传统编程模型,是异步的
- 围绕响应变化而构建的编程模型-网络组件响应I / O事件
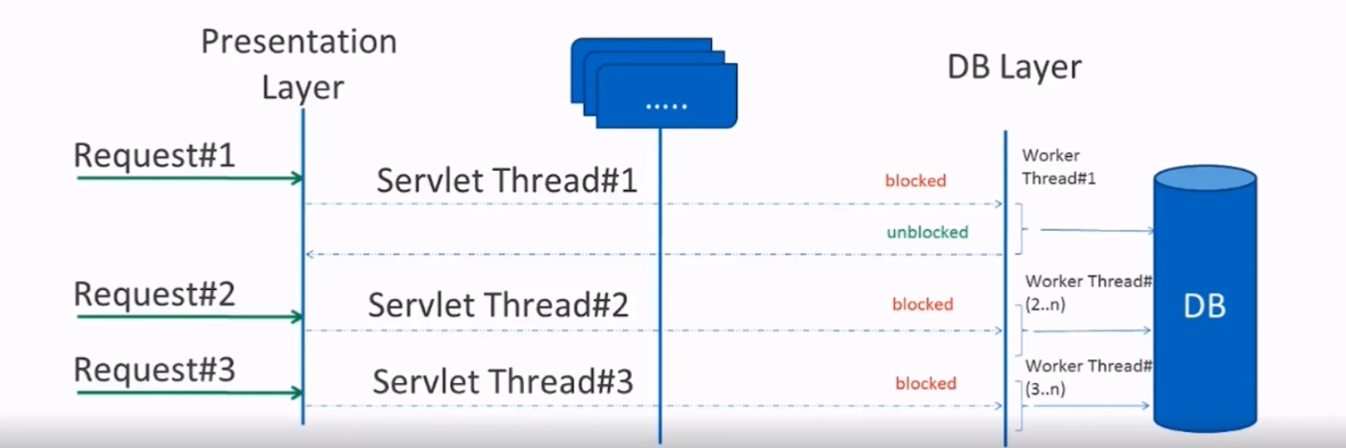
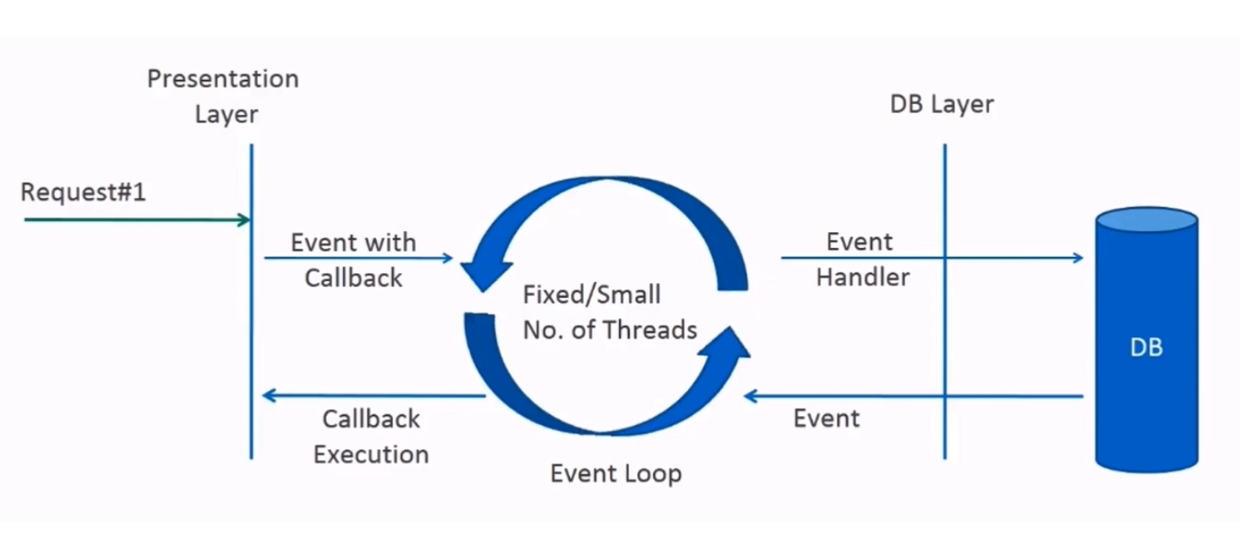
概念
响应式api
- 接收Publisher作为输入
- Flux或者Mono作为输出
编程模型
web flux提供了两种编程模型:
- 带注释的controller:和经典的web mvc一样
- 功能端点:从到到尾由应用程序自己路由、处理请求。和nodejs一样
web mvc or web flux?
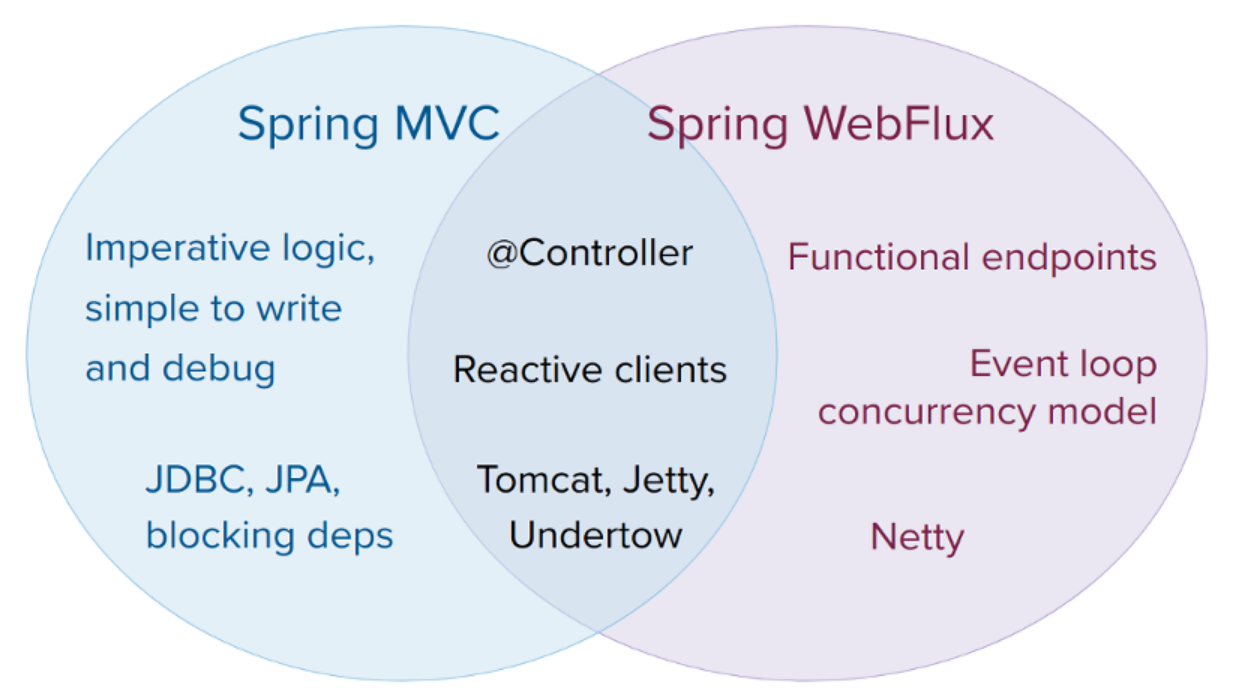
服务器
在 web flux中,可以跨tomcat、jetty等容器使用
性能
非阻塞方式进行操作需要更多的工作,这可能会稍微增加所需的处理时间使用响应式的好处在于能够以较少的固定数量线程以及更少的内存资源进行更好的扩展
并发模型
- 调用阻塞api:虽然一些方法可以在响应式编程中使用,但会引入一些额外的问题
- 可变状态:通过运算符,形成一个响应式管道,在不同的阶段处理数据
- 线程模型
- 原始线程模型
- 事件循环
- 调度程序
- 配置
- 不同的服务器的配置需要使用各自服务器的api
响应式核心
HttpHandler
一个可以处理请求并且响应的单一方法不同的服务器具有不同的api
WebHandler
spring web基于httphandler封装了WebHandler
Filters
可以使用 WebFilter 处理请求
Exceptions
可以使用ExceptionHandler来处理请求与响应中的异常
Codecs
web flux 提供了一些封装来负责数据的序列化与反序列化
DispatcherHandler
类似于mvc中的DispatcherServlet
负责对请求的统一控制与转发
使用
传统方式
跟MVC一样 可以使用controller等相关注解进行使用
函数式端点
概览
class Handler { public Mono<ServerResponse> listPeople(ServerRequest request) { // ... } public Mono<ServerResponse> createPerson(ServerRequest request) { // ... } public Mono<ServerResponse> getPerson(ServerRequest request) { // ... }}Handler handler = new Handler();// 定义路由映射RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = route() .GET("/person/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::getPerson) .GET("/person", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::listPeople) .POST("/person", handler::createPerson) .build();ServerRequest
提供了一个访问请求数据的东西
Mono<String> string = request.bodyToMono(String.class);ServerResponse
这玩意是不可变的,所以需要手动来创建
public Mono<ServerResponse> listPeople(ServerRequest request) { return ok().body(Mono.just("people list"), String.class);}路由判断
// 只有person/1才会被处理route().GET("/person/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON).and(request-> "1".equals(request.pathVariable("id"))), handler::getPerson)路由优先级
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = route() .GET("/person/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::getPerson) //1 .GET("/person", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::listPeople) // 2 .POST("/person", handler::createPerson) // 3 .add(otherRoute) // 添加其他路由 .build();嵌套路由
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = route() .path("/person", builder -> builder .GET("/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::getPerson) .GET("", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::listPeople) .POST("/person", handler::createPerson)) .build();运行
- spring boot
@EnableWebFlux@BeanRouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction(){ ...}过滤器
route() .before(req->{ System.out.println(req.path()+"before"); return req; }) .GET("/person/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON).and(request-> "1".equals(request.pathVariable("id"))), handler::getPerson) .GET("/person", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::listPeople) .POST("/person", handler::createPerson) .after((req,res)->{ System.out.println(req.path()+"after"); return res; }) .build();或者另外一种方式:
route() .GET("/person/{id}", accept(APPLICATION_JSON).and(request-> "1".equals(request.pathVariable("id"))), handler::getPerson) .GET("/person", accept(APPLICATION_JSON), handler::listPeople) .POST("/person", handler::createPerson) .filter((req,res)->{ System.out.println(req.path()+"before"); return res.handle(req); }) .build();